GDPR, HIPAA, PCI & CCPA: What Engineering Teams Need to Know

Let's be honest, when someone mentions "compliance," most developers and security teams inwardly groan. The word brings to mind endless spreadsheets, auditor checklists, and dense legal language that feels miles away from actual code.
But here's the thing: in 2026, compliance isn't just some legal box to check. It's become an operational survival skill. One small logging mistake that captures a user's IP address? That could be a GDPR violation. An unencrypted database backup sitting somewhere? Hello, HIPAA breach. A forgotten development server still holding real credit card numbers? Your payment processing could get shut down overnight.
This article breaks down the four major regulatory frameworks that every engineering team needs to understand, not through a legal lens, but through a technical one. Let's dive in.
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
The Global Privacy Standard
Who it affects: Pretty much anyone who processes data from people living in the European Union. Doesn't matter where your company is headquartered, if you've got EU users, you're in scope.
What it's trying to do: Give users real control over their personal data. Not just lip service, but actual, enforceable control.
Key Technical Requirements
The "Right to be Forgotten" (Article 17)
This one's a technical headache if you haven't planned for it. When someone asks to be deleted, you can't just remove them from your main database and call it a day. You need to scrub their PII from everywhere, production databases, backups, logs, third-party analytics tools, the works.
This is why data architects who plan for deletion from day one are worth their weight in gold.
Data Minimization
You can't just collect data "because we might need it someday." If you don't actually need a phone number for your service to function, collecting it puts you in violation territory. Every field in your signup form should have a clear justification.
Breach Notification (72 Hours)
If you leak data, the clock starts ticking immediately. You've got 72 hours to report it. This means your detection systems, SIEM, IDS, whatever you're using, need to be running in real-time. You can't wait for some monthly security audit to uncover a breach that happened three weeks ago.
The Stakes
Fines up to €20 million or 4% of global annual revenue, whichever hurts more. Meta got hit with a €1.2 billion fine in 2023. These aren't theoretical penalties, regulators are actually enforcing them.
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)
The Health Shield
Who it affects: Healthcare providers, insurance companies, and anyone who works with them, including tech vendors, cloud providers, and SaaS applications. If you're a "Business Associate," you're on the hook too.
What it's trying to do: Protect ePHI, Electronic Protected Health Information. Basically, any digital health data about a real person.
Key Technical Requirements
Encryption Everywhere
Not optional, not negotiable. Data must be encrypted at rest (AES-256 is the standard) and in transit (TLS 1.3 or better). There's no "but we're a small startup" exception here.
Strict Access Control
The "Least Privilege" principle isn't just a best practice under HIPAA, it's the law. Your database admin shouldn't have access to patient records unless they specifically need them for a particular task. Role-based access control isn't fancy; it's fundamental.
Audit Trails
You need logs of who accessed what data, and you need to keep those logs for at least 6 years. If someone views a medical record, there better be a timestamped entry showing it. No logs, no compliance.
The Stakes
Fines can reach $1.5 million per year per violation category. And in extreme cases of negligence, criminal charges are on the table. This is serious stuff.
PCI-DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard)
The Money Guard
Who it affects: Anyone who accepts, processes, stores, or transmits credit card information. If you see card numbers, you're in scope.
What it's trying to do: Secure cardholder data to prevent fraud and protect consumers.
Key Technical Requirements
Scope Reduction
Here's the smartest way to comply with PCI-DSS: don't touch the data in the first place. Use tokenization services like Stripe Elements so that raw card numbers never hit your servers. Can't leak what you don't have.
No CVV Storage
This is an absolute rule with zero wiggle room. You are strictly forbidden from storing the CVV/CVC code (those 3 or 4 digits on the card) after authorization. Not encrypted, not hashed, not anything. If auditors find stored CVVs, you instantly fail compliance.
Network Segmentation
Your cardholder data environment (CDE) needs to live on a separate network segment, completely isolated from your corporate Wi-Fi, guest networks, or anything else. This isn't paranoia, it's defense in depth.
The Stakes
Monthly fines ranging from $5,000 to $100,000, increased transaction fees that eat into your margins, and in the worst case scenario, the "death penalty" of losing your ability to process credit cards entirely. For an e-commerce business, that's game over.
CCPA / CPRA (California Consumer Privacy Act)
The US Privacy Standard
Who it affects: Companies doing business in California that hit certain revenue or data volume thresholds. But here's the reality: because California's economy is so massive, this has become the de facto national standard for privacy in the US.
What it's trying to do: Give consumers transparency and control over how their personal data is sold or shared.
Key Technical Requirements
"Do Not Sell My Data"
You must provide a clear, easy-to-find mechanism (typically a footer link) for users to opt out of data sharing. It needs to be functional, not just decorative.
Data Mapping
You need to know exactly where user data flows through your systems. If a user asks "What do you know about me?", you have 45 days to produce a comprehensive report of all their data categories. No guessing allowed.
Vendor Management
Here's where it gets tricky: you're responsible for making sure your third-party vendors, advertisers, analytics platforms, all of them, also respect user opt-outs. Their compliance failures become your compliance failures.
The Stakes
Civil penalties of $2,500 per unintentional violation and $7,500 per intentional violation. Now multiply that by millions of users in a class-action lawsuit, and you're looking at billions in potential exposure.
The Importance of Data Visibility
When you look at these four frameworks side by side, one theme keeps coming up: You cannot secure what you cannot see.
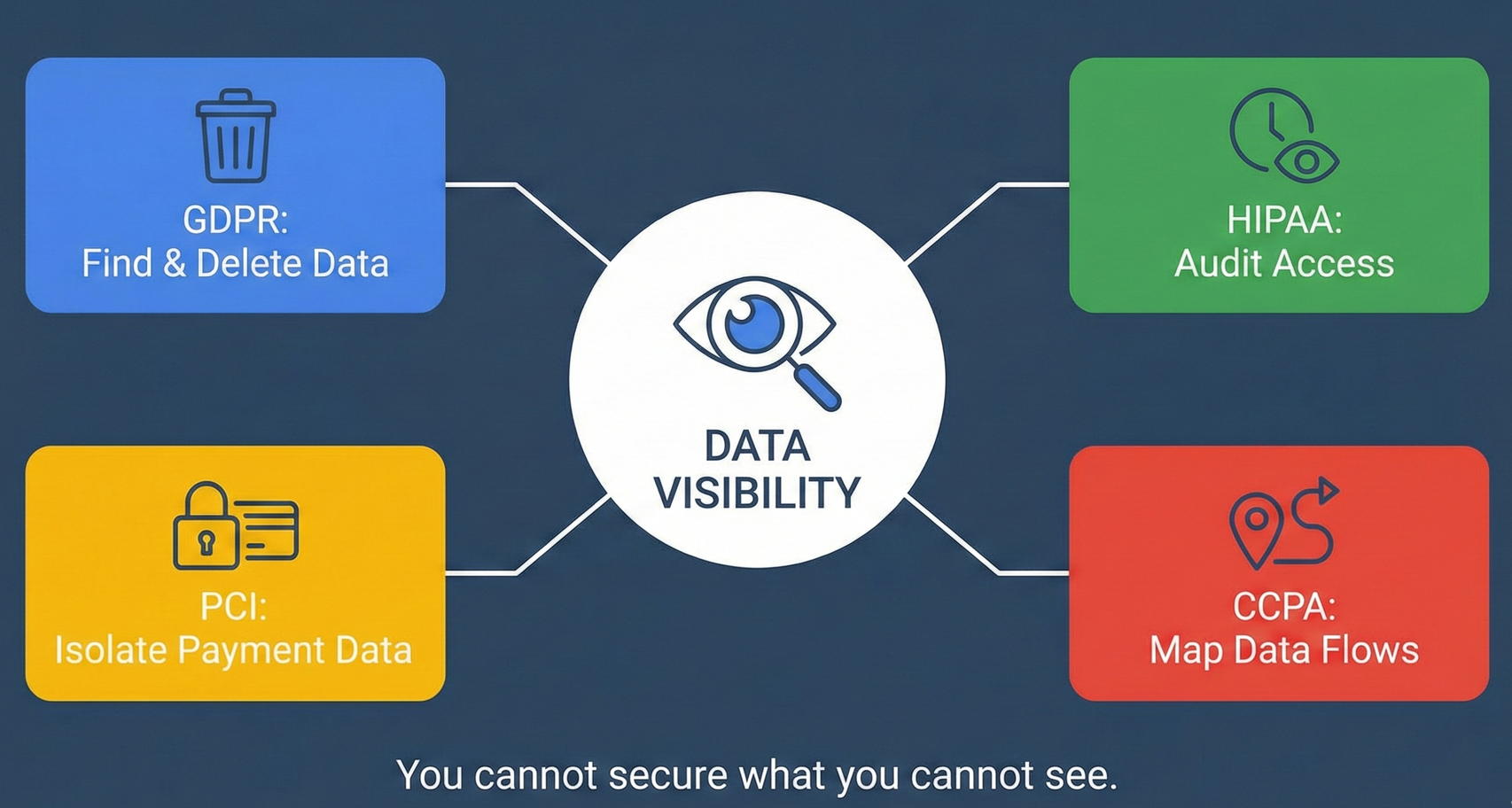
- GDPR requires you to find and delete user data across your entire infrastructure
- HIPAA requires you to audit who's accessing health data and when
- PCI requires you to isolate payment data in a secure environment
- CCPA requires you to map data flows and know where everything goes
If your organization has "shadow APIs" or forgotten S3 buckets sitting around with old user backups, you're already non-compliant, you just don't know it yet. The first step toward compliance isn't writing a policy document or hiring a consultant. It's discovering your data. All of it.
How We Can Help
In 2026, compliance isn't just about policies and procedures, it's about having real-time visibility into your data. You can't comply with GDPR if you don't know where your user data actually lives. You can't meet HIPAA requirements if you can't track who's accessing what. You can't satisfy PCI auditors if you're not sure which systems touch card data.
Jsmon.sh helps you map your data exposure in real-time. Our advanced scanning engine detects leaked PII, unencrypted secrets, and sensitive data patterns across your entire attack surface, before the auditors find them. Or worse, before the attackers do.
Secure your business, in real-time!
Technical References:
- https://www.pentasecurity.com/blog/4-data-compliance-standards-gdpr-hipaa-pci-dss-ccpa/
- https://www.netapp.com/blog/data-compliance-regulations-hipaa-gdpr-and-pci-dss/
- https://compliancy-group.com/what-is-hipaa-compliance/
- https://gdpr.eu/
- https://www.pcisecuritystandards.org/
- https://oag.ca.gov/privacy/ccpa