
What is Broken Access Control? Ways to Exploit, Examples and Impact
Explore Broken Access Control, IDOR, and privilege escalation. Learn how to exploit and prevent the #1 OWASP vulnerability with technical code examples.

Explore Broken Access Control, IDOR, and privilege escalation. Learn how to exploit and prevent the #1 OWASP vulnerability with technical code examples.
Discover how race conditions work, see real-world exploit examples like TOCTOU, and learn how to secure your code against concurrency vulnerabilities.

Explore webhook vulnerabilities like SSRF and replay attacks. Learn technical exploitation methods and best practices to secure your callback endpoints.
Understand the GraphQL N+1 problem, its security impact, and how to prevent Denial of Service attacks with DataLoaders and query complexity analysis.
Understand GraphQL batching attacks, explore exploitation examples like brute force, and learn how to secure your API against these common vulnerabilities.
Understand GraphQL introspection risks, exploitation techniques, and mitigation steps. Secure your API schema from information disclosure today.
Master the fundamentals of API Injection. Explore technical examples of SQLi, NoSQLi, and Command Injection, and learn how to secure your API endpoints.
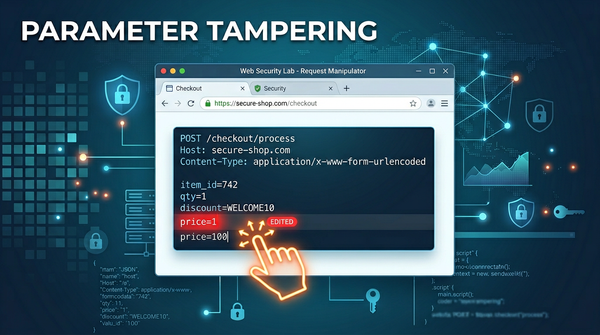
Learn how parameter tampering works, see real-world exploitation examples, and discover how to prevent this critical web vulnerability.
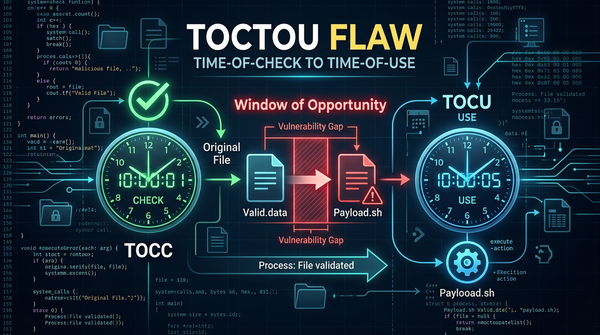
Discover how Time-of-Check to Time-of-Use (TOCTOU) flaws create race conditions. Learn to identify, exploit, and mitigate these vulnerabilities in your code.

Discover common business logic flaws, real-world exploit examples, and prevention strategies to secure your web applications against logical attacks.

Master the risks of Improper Assets Management and Shadow APIs. Learn how attackers exploit undocumented endpoints and how to protect your infrastructure.

Deep dive into Rate Limiting and Resource Exhaustion. Learn technical exploitation, bypass techniques, and how to secure your APIs against automated attacks.